The urgency for organizations to transform themselves in the face of technology-fueled disruption has been a critical challenge in many industries. In the banking sector, incumbent players are dealing with the emergence of financial technology, or fintech, firms that threaten them in a range of business segments. One bank that has taken this challenge head-on is Singapore-based DBS Group, which embarked on an organization-wide transformation in 2009 (Bawany 2020).
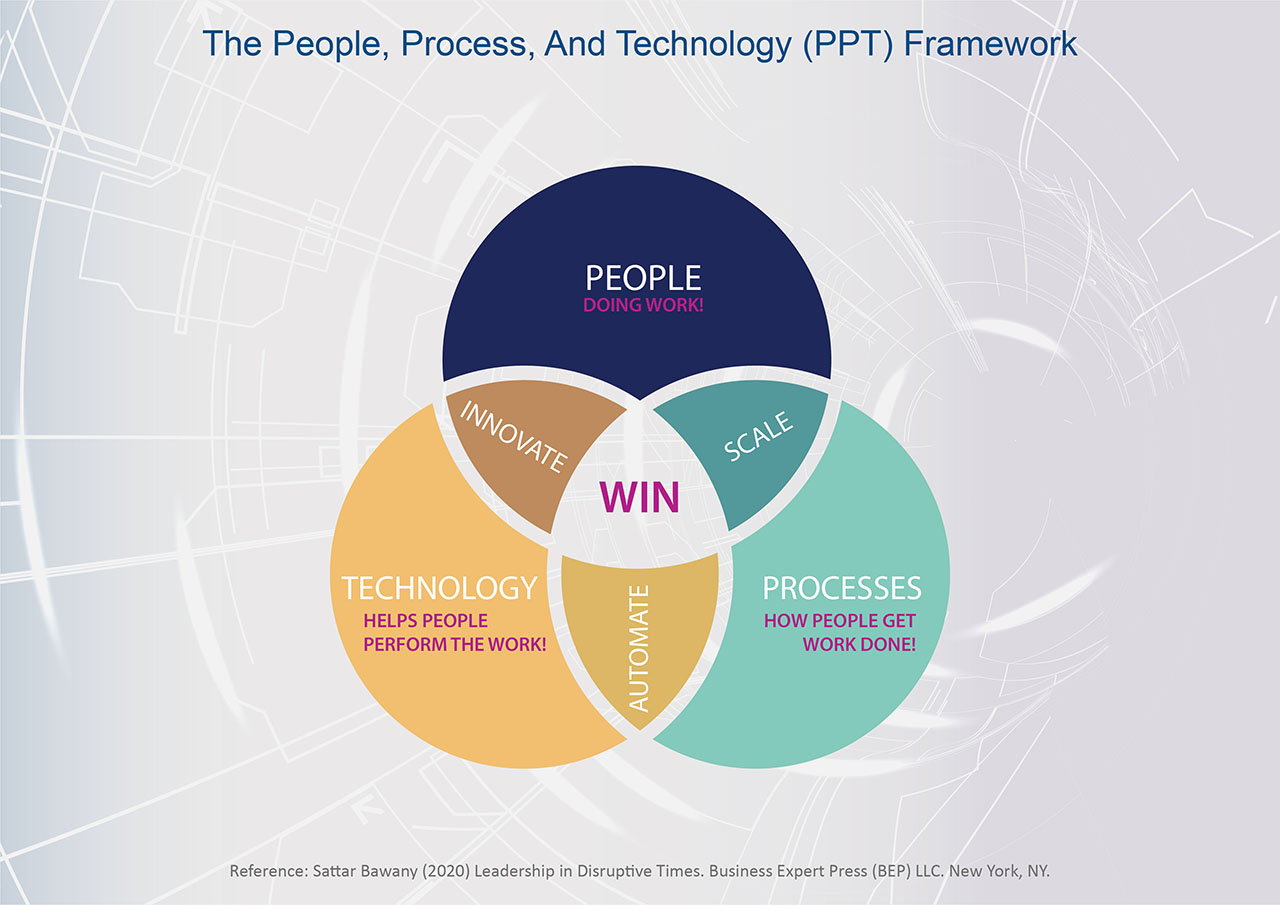
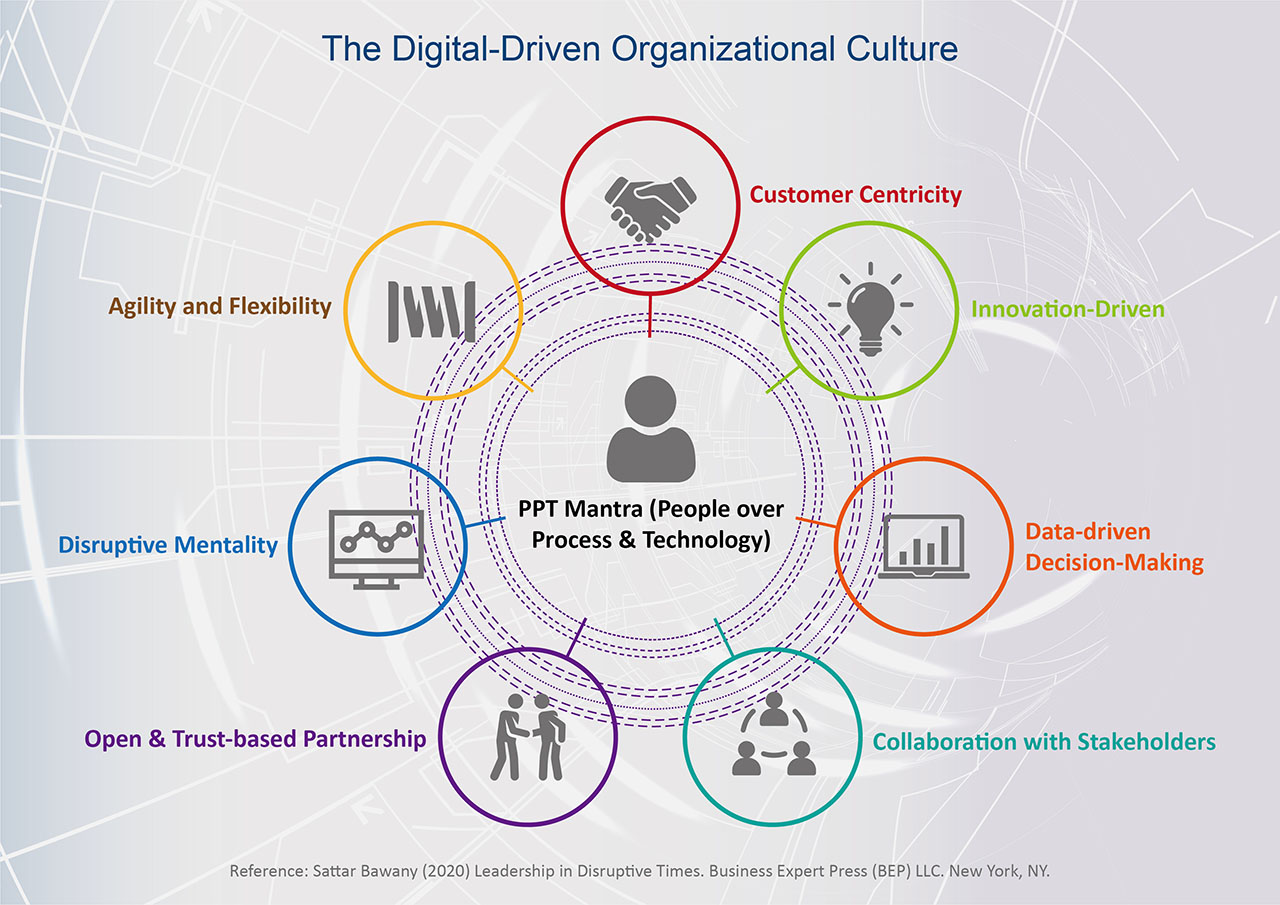
As DBS embarks on DT/DX at the workplace, the CEO, Piyush Gupta create a culture in which everyone is digitally savvy and demonstrates a set of values, competencies, and practices where they can continuously seek to redefine how they create and deliver value for customers by leveraging on digital technologies. These would include customer-centricity, innovation-driven, data-driven decision-making, intra & inter-team collaboration, an open and trust-based partnership, disruptive mentality, and agility and flexibility in managing challenges (see Figure 2).
To change behaviors, the transformation team settled on five key traits or DNA for the digital culture: agility, being a learning organization, being customer-obsessed, being data-driven, as well as experimenting (innovation), and taking risks. The team targeted inefficient meetings as a barrier to change and a hindrance to innovation. Meetings often started and ran late without leading to decisions. Worse, meetings often lacked purpose and were dominated by a few voices, while others sat in defensive silence. In 2019, DBS was ranked by Harvard Business Review as being among the top 10 companies in the world to have made successful strategic transformations in the last decade.
In addition to transforming customer-facing applications, DBS also uses digital to empower its employees, helping them to work smarter and driving gains in efficiency and productivity. Moreover, employee-focused aspects of digital complement efforts to improve the banking experience for consumers. By providing more and better digital services, DBS can capture data and generate a refined, high-resolution profile of its customers’ preferences and behaviors. Still, that data is meaningless unless employees can readily access it and use it to improve the bank’s offerings.
At DBS, people are the key differentiator, forming the cornerstone of the bank transformation strategy, as it aspired to cultivate its people to embrace start-up qualities of being customer-obsessed, data-driven, risk-taking, agile, and continually learning. The bank is passionate about being a learning organization and has created a culture that allows the people a myriad of opportunities to learn, reskill, and upskill to equip them with digital capabilities,
especially its legacy workforce, some of whom had been with the bank for over 30 years.
As part of the DT/DX strategy, the bank focuses on changing its culture to a start-up culture by being “Agile,” focusing relentlessly on the customer, using data to help the employees make better decisions, being digital to the core, and continuously experimenting and innovating to improve and enhance its corporate sustainability. One of the initiatives that the bank implemented was to experiment with agile workspaces by adopting “Design Thinking” and creating what is known as JoySpace, which enables the employees to work in squads for better collaboration and ideation, breaking down silos, and focusing relentlessly on the customer.