Introduction to the Results-Based Leadership (RBL) Framework
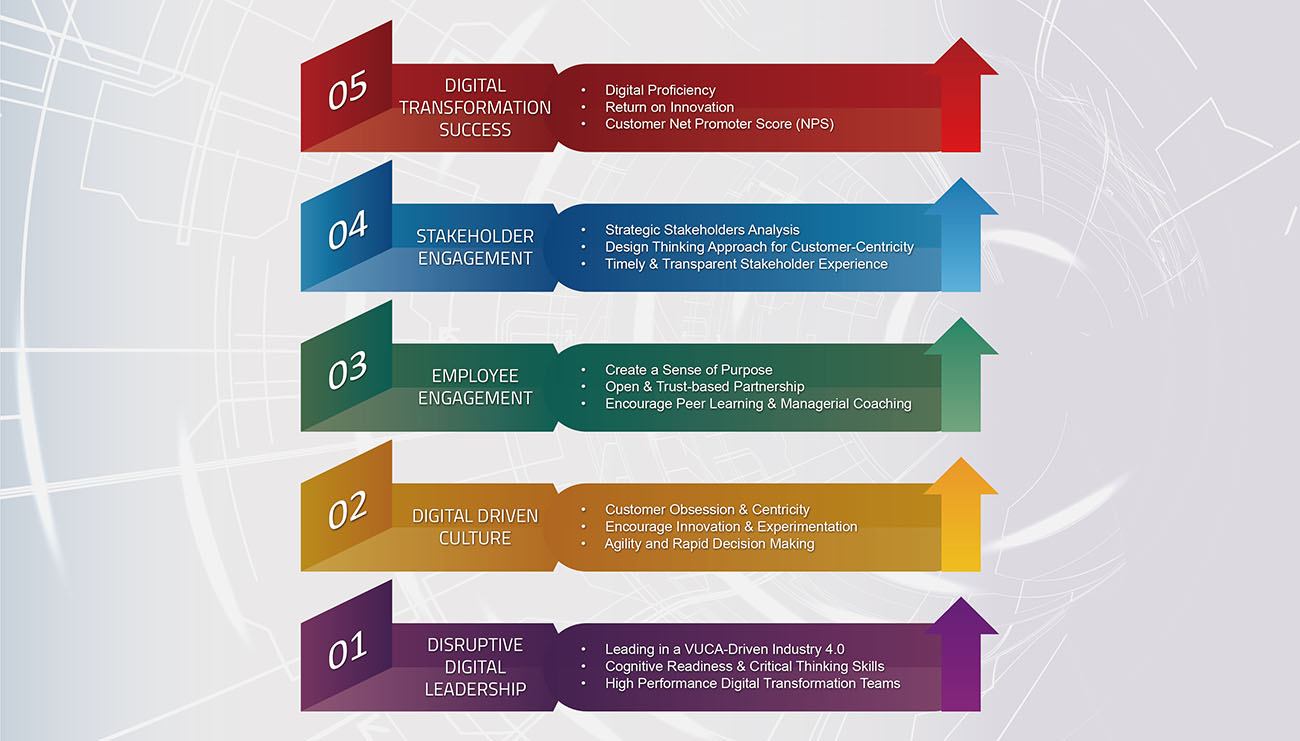
Figure 1: The Results-Based Leadership (RBL) Framework
There is currently extensive published research on the direct link between leadership effectiveness and sustained organizational performance. Hence, the development of the disruptive leader’s capability should be of primary concern for all organizations operating in Industry 4.0, since the contribution and motivation of the employees are key to achieving the organizational goals and objectives. While all organization needs financial resource, technical and professional knowledge and expertise, relevant systems, and processes, success cannot be assured and sustained unless the leaders can utilize these resources creatively and effectively. Arguably, the organizations that are best placed to survive and thrive in the disruptive business environment of Industry 4.0 are those which have a strong focus on leadership development practices and a good understanding of what effective leadership means to them (Bawany 2020).
In the Results-Based Leadership (RBL) Framework (See Figure 1) developed by the Centre for Executive Coaching (CEE), disruptive and crisis leaders must focus on effectively engaging all stakeholders, in particular, the employees, in delivering sustainable results for their organization. In the era of the Industry 4.0 workplace and at a time of continued significant transition and challenge, leaders at all levels will have a responsibility to ensure that the organization’s mission and purpose are at the heart of what they do.
The concept of “engagement” can be defined in many ways. Essentially, engagement is a measure of how an organization values its employees and how employees value their organization and recognize that every individual is at liberty to decide whether to do the minimum required of them or to do more. Engagement can also be taken to represent the degree of empowerment to which staff are involved in decision making and/or the openness and perceived effectiveness of communication. Hence, leaders at all levels have a key role in cultivating a strong culture of engagement. This, in essence, is the foundation of the “results-based leadership” (RBL) framework for a digital-driven organization.
Step 1: The basic premise of the RBL framework is that a highly effective transformational disruptive digital leader would start with a strong sense of self-leadership, in particular, developing a high level of self-awareness of his or her strengths and area of development in the crucial competencies for a disruptive digital leader as discussed in the preceding chapter. These include but are not necessarily limited to agility, adaptability, emotional resilience and social skills, empathy, cognitive readiness, critical thinking, driving for results, innovativeness, and resilience. Next, he or she needs to lead and engage the team by coaching them to success by adopting the proven SCORE™ High-Performance Team Framework, which can be found in Chapter 9 of the book, Leadership in Disruptive Times: Negotiating the New Balance. (2023)
Step 2: Organizational climate (sometimes known as corporate climate) simply refers to how employees feel about working in the organization. Organizational climate is the process of quantifying the culture of an organization. It is a set of properties of the work environment, perceived directly or indirectly by the employees, that is assumed to be a major force in influencing employee behavior and engagement. By implementing step 1 effectively along with the relevant contemporary human resource practices such as flexible work arrangements like “work from anywhere” (WFA) including workplace flexibility, flexible work hours, telecommuting, and “work from home,” the leader will create an organizational climate of an open trust-based partnership between themselves and the employees who will be highly engaged and would want to remain in the organization, especially those who have highly marketable talent.
Step 3: The level of employee engagement is dependent on the organizational climate. Employees who are engaged and motivated are instrumental in delivering the required customer service experience for the client, which will result in customer engagement and retention. Consequently, engaged employees will result in employee loyalty, which will reduce the attrition rate and the operating costs of hiring new staff.
Step 4: Employees who feel fully committed to the organization for which they work take great pride in doing their job. They do more than is expected of them and go that extra mile. In so doing, engaged employees, in particular, the frontline service staff or customer-interfacing employees, will have an impact and inevitably influence the buying behaviors of the customers. The excitement of an engaged employee is contagious and cannot help but rub off on the customer.
Step 5: The digital business KPIs or metrics of success for the high-performance digital organization differ for each organization. They may include percentage of digital customer interactions, percentage of marketing spend that is digital, and percentage of revenue through digital channels among others.
However, one of the factors driving profitability and efficiency is the level of customer engagement or loyalty, since the cost of acquisition of new customers is reduced significantly. Loyalty is a direct result of customer satisfaction. Satisfaction is largely influenced by the value of services provided to customers. Value is created by satisfied, loyal, and productive employees, especially customer-interfacing service employees. Employee satisfaction, in turn, results primarily from the internal high-quality support services and organizational policies that enable the frontline team to deliver excellent service to customers.
Managers often fail to appreciate how profoundly the organizational climate can influence financial results. It can account for nearly a third of financial performance (Goleman 2000). Organizational climate, in turn, is influenced by leadership style and by the way or manner in which the leader motivates direct reports, gathers and uses information, makes decisions, manages change initiatives, and handles crises.
The fundamentals remain that all organizations, including those digitally driven, need to continuously deliver service value and build good customer relationships to generate sustainable results through their satisfied and loyal customers. Employees being at the forefront of the service delivery chain hold the key to building this satisfied and loyal customer base.
Importance of Communication Skills for Disruptive Leaders
Developing excellent communication skills is essential to effective disruptive leadership. The leader must be able to share knowledge and ideas to transmit a sense of urgency and enthusiasm to others during the implementation of digital transformation initiatives. If a leader can’t get a message across clearly and motivate others to act on it, then having a message doesn’t even matter. Disruptive leadership also means communicating with others, so they are influenced and motivated to perform actions that further common goals and lead toward desired outcomes.
Communication is the key to driving successful digital transformation in the workplace. It helps disruptive leaders connect with employees, keep the workforce abreast of changes so they can move with them, and empowers staff to adapt and learn to stay current and focused. A successful disruptive leader must also bear in mind that while technology is important, the people part of the transformation is just as crucial. They can better impact and influence their team members if they possess excellent communication skills and avoid possible conflicts. Communication is the key to generating workforce willingness. It is the lever that helps leaders change beliefs, cultivate understanding, and create buy-in. In successful transformations, leaders connect with and gain the full support of the workforce with authentic, compelling, and consistent communication.
To achieve extraordinary success in leadership, the digital leader not only needs a clear vision of the digital transformational goals and objectives but also to know how to communicate these objectives to team members and other stakeholders. Hence, effective communication is an essential element of leadership. Disruptive leaders are communication champions who inspire and unite people around a common sense of purpose and identity. They lead strategic conversations that get people talking across boundaries about the vision, key strategic themes, and the values that can help the group or organization achieve desired outcomes (Bawany 2014f).
The strategic conversation is communication that takes place across boundaries and hierarchical levels about the group or organization’s vision, critical strategic themes, and values that can help achieve desired outcomes. This is achieved by actively listening to others to understand their attitudes and values, needs, personal goals, and desires, as well as selecting the right communication channels and facilitating dialogue. Inspiring someone without effective communication is almost impossible.
Leaders must keep in mind that all good organizations achieve their goals through effective communication at all levels of the organization. To achieve this, they have an organized system of communicating at different levels of the organization.
As technology continues to disrupt the workplace, one of the key factors that would impact the success of the digital transformation is the talented employees, including the leaders, who can use existing digital technologies and adapt to evolving methods and new approaches. Without them, organizations will struggle to benefit as they should from the latest advances in Industry 4.0—everything from robots to AI, data science, virtual reality, blockchain technologies, cloud computing, the Internet of Things, and new digital business models.
Even if the technologies themselves are evolving and relatively easily acquired and deployed, having the right team of disruptive leaders who can lead the digital transformation implementation successfully will be scarce. Digitally talented people are already so highly in demand that many large, traditional companies must reinvent themselves to attract them.
Organizations should respond to this challenge by building new pools of skilled digital talent. To do so, they must identify the skills and attributes of these high-potential employees and assess and develop them into disruptive leaders who will lead successful digital transformation initiatives (Bawany 2020).
Reference: Sattar Bawany (2023), Leadership in Disruptive Times: Negotiating the New Balance. Business Expert Press (BEP) LLC, New York, NY. Abstract available at: https://www.disruptiveleadership.institute/second-edition-book/